最新下载
热门教程
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
python多线程中join()的作用代码示例解析
时间:2020-10-29 编辑:袖梨 来源:一聚教程网
本篇文章小编给大家分享一下python多线程中join()的作用代码示例解析,文章代码介绍的很详细,小编觉得挺不错的,现在分享给大家供大家参考,有需要的小伙伴们可以来看看。
multiprocessing 是python提供的跨平台版本的多进程模块。multiprocessing可以充分利用多核,提升程序运行效率。multiprocessing支持子进程,通信和共享数据,执行不同形式的同步,提供了Process、Queue、Pipe、Lock等组件。
join()方法可以在当前位置阻塞主进程,带执行join()的进程结束后再继续执行主进程的代码逻辑。
# encoding: utf-8
"""
author: yangyi@youzan.com
time: 2019/7/30 11:20 AM
func:
"""
from multiprocessing import Process
import os
import time
def now():
return str(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.localtime()))
def func_1(name):
print(now() + ' Run child process %s (%s)...' % (name, os.getpid()))
time.sleep(4)
print(now() + ' Stop child process %s (%s)...n' % (name, os.getpid()))
def func_2(name):
print(now() + ' Run child process %s (%s)...' % (name, os.getpid()))
time.sleep(8)
print(now() + ' hello world!')
print(now() + ' Stop child process %s (%s)...n' % (name, os.getpid()))
if __name__ == '__main__':
print ('Parent process %s.' % os.getpid())
p1 = Process(target=func_1, args=('func_1',))
p2 = Process(target=func_2, args=('func_2',))
print now() + ' Process start.'
p1.start()
p2.start()
p1.join()
p2.join()
print now() + ' Process end .'
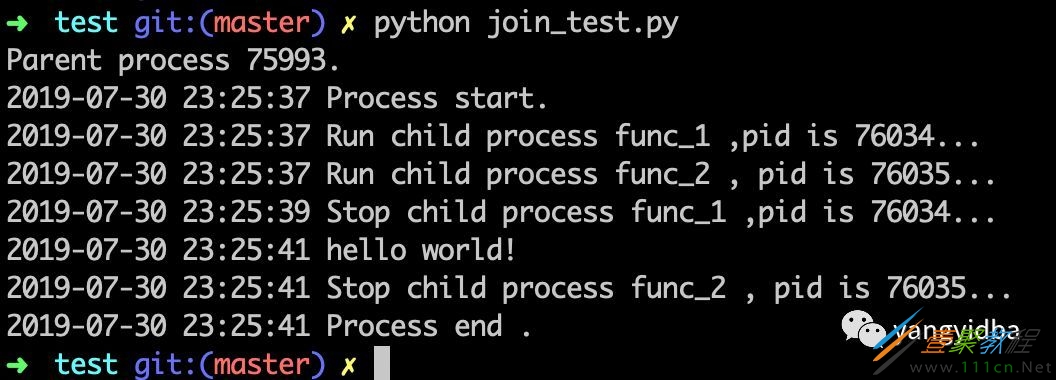
输出结果
结果显示
主进程的 Process end .是在func1 和func2 结束之后才打印出来的。
去掉 join() 函数
if __name__ == '__main__':
print ('Parent process %s.' % os.getpid())
p1 = Process(target=func_1, args=('func_1',))
p2 = Process(target=func_2, args=('func_2',))
print now() + ' Process start.'
p1.start()
p2.start()
print now() + ' Process end .'
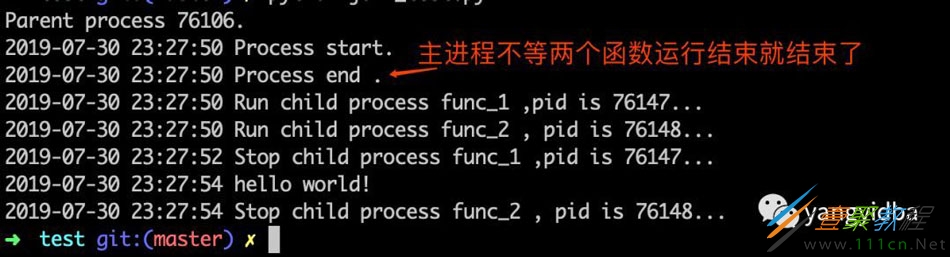
结果如下:
去掉func_2 的 join()
if __name__ == '__main__':
print ('Parent process %s.' % os.getpid())
p1 = Process(target=func_1, args=('func_1',))
p2 = Process(target=func_2, args=('func_2',))
print now() + ' Process start.'
p1.start()
p2.start()
p1.join() ### 在p1 执行完之后 。不等待p2 执行,主进程结束。
print now() + ' Process end .'
结果如下:
结果显示主线程 "Process end"在func_1 执行结束之后输出而没有等待func_2 执行完毕。
相关文章
- Golang ProtoBuf的基本语法详解 10-20
- Python识别MySQL中的冗余索引解析 10-20
- Python+Pygame绘制小球代码展示 10-18
- Python中的数据精度问题介绍 10-18
- Python随机值生成的常用方法介绍 10-18
- python3解压缩.gz文件分析 09-27